
Introduction
5G is the next generation of wireless technology that promises to revolutionize connectivity. It is expected to deliver much faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than previous generations of wireless technology. This will make it possible for a wide range of new applications and services, such as streaming high-definition video, self-driving cars, and virtual reality.
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, following 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G. It is a major step up from previous generations in terms of speed, latency, and capacity.
Speed
5G is expected to deliver peak speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps). This is more than 100 times faster than the average speed of 4G networks.
Latency
Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from one point to another. 5G is expected to have a latency of less than 1 millisecond, which is comparable to the speed of light. This will make it possible for real-time applications such as self-driving cars and virtual reality.
Capacity
5G networks are expected to have a much greater capacity than previous generations. This will allow them to support a much larger number of devices and users.
Benefits of 5G
The faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity of 5G will make it possible for a wide range of new applications and services. These include:
- Streaming high-definition video
- Self-driving cars
- Virtual reality
- Remote surgery
- Industrial automation
- Smart cities
Applications of 5G
5G is still in its early stages of development, but it is already being used in a variety of applications. These include:
- Mobile gaming
- Virtual reality
- Streaming high-definition video
- Remote surgery
- Industrial automation
- Smart cities
Challenges of 5G
There are a number of challenges associated with 5G. These include:
- The high cost of deploying 5G networks
- The need for new spectrum
- The need for new devices
- The need for new security measures
5G Timeline
5G is still in its early stages of development, but it is expected to be widely available by 2025.
5G Standardization
The 5G standard is being developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). The first 5G standard was released in 2018, and the second 5G standard is expected to be released in 2020.
5G Security
5G networks will be more vulnerable to security threats than previous generations of wireless networks. This is because 5G networks will be more complex and will use new technologies that have not been fully tested.
5G Cost
The cost of deploying 5G networks is expected to be high. This is because 5G networks will require new infrastructure and new devices.
FAQ
| 5G | Evolution, Connectivity, Trends, Techniques |
|---|---|
| Introduction | 5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, and it promises to revolutionize connectivity. |
| What is 5G? | 5G is a new wireless technology that offers significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than previous generations of wireless technology. |
| Benefits of 5G | 5G has a number of benefits over previous generations of wireless technology, including:
|
| Applications of 5G | 5G has a wide range of potential applications, including:
|

II. What is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, and it promises to deliver significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than previous generations. 5G is expected to revolutionize the way we live and work, enabling new applications such as self-driving cars, virtual reality, and augmented reality.
III. Benefits of 5G
5G is expected to bring a number of benefits to businesses and consumers, including:
- Increased speed: 5G networks are expected to be up to 100 times faster than current 4G networks, which will allow for faster downloads, streaming, and gaming.
- Lower latency: 5G networks will also have much lower latency, meaning that data can be transmitted more quickly and reliably. This will be beneficial for applications such as self-driving cars and remote surgery.
- Greater capacity: 5G networks will be able to support more devices than current networks, which will be important as the number of connected devices continues to grow.
- Improved coverage: 5G networks will provide better coverage than current networks, even in rural areas. This will make it possible for more people to access high-speed internet.
5G is still a relatively new technology, but it is already showing great potential to revolutionize the way we live and work. As 5G networks continue to roll out, we can expect to see even more benefits in the years to come.

IV. Applications of 5G
5G is expected to have a wide range of applications, including:
- Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB): This will provide faster speeds and lower latency for mobile devices, allowing users to stream high-definition video, download large files, and play online games with ease.
- Massive machine-type communications (mMTC): This will enable a large number of devices to connect to the network and exchange data, such as sensors in industrial settings or connected cars.
- Ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC): This will provide guaranteed service levels for applications that require very low latency, such as self-driving cars or industrial automation.
5G is expected to revolutionize the way we live and work, making it possible for us to connect to the world in new and innovative ways.
V. Challenges of 5G
There are a number of challenges associated with the development and deployment of 5G technology. These include:
- High cost: 5G networks are more expensive to build and operate than previous generations of wireless networks. This is due to the need for more base stations and higher-bandwidth spectrum.
- Spectrum scarcity: There is a limited amount of available spectrum that can be used for 5G networks. This means that governments and regulators need to carefully manage the allocation of spectrum to ensure that it is used efficiently.
- Security: 5G networks are more vulnerable to security threats than previous generations of wireless networks. This is due to the increased complexity of 5G networks and the fact that they will be used to connect a wider range of devices.
- Energy efficiency: 5G networks require a lot of energy to operate. This is because they need to transmit data at high speeds and over long distances.
- Latency: 5G networks need to have very low latency in order to support real-time applications such as self-driving cars and virtual reality. This can be a challenge, especially in congested areas.
Despite these challenges, 5G is still a promising technology with the potential to revolutionize connectivity. By addressing the challenges outlined above, 5G networks can deliver the high speeds, low latency, and reliability that are needed to support the next generation of mobile applications.
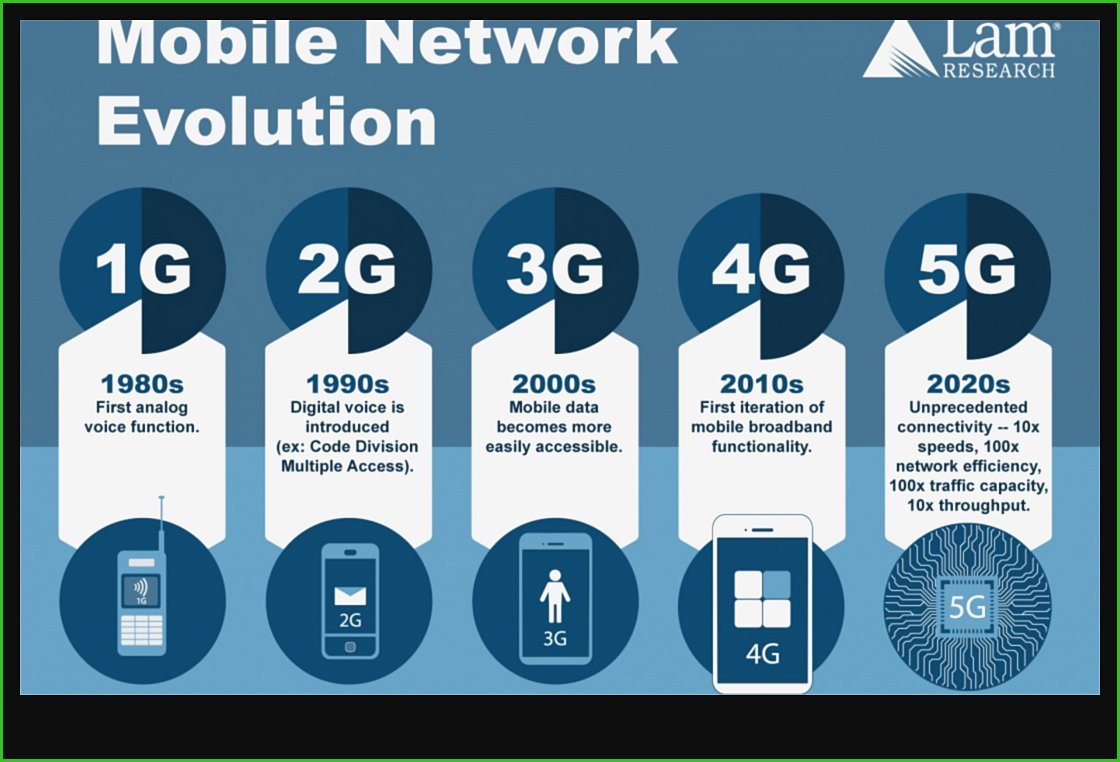
VI. 5G Timeline
The development of 5G has been a long and complex process, with many different standards and technologies being considered. The following is a timeline of some of the key milestones in the evolution of 5G:
- 2010: The first 5G research projects are launched in Europe and the United States.
- 2012: The first 5G test networks are established in South Korea and Japan.
- 2014: The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) releases the first 5G standard, Release 15.
- 2016: The first commercial 5G networks are launched in South Korea and the United States.
- 2018: The 3GPP releases Release 16, which includes new features for 5G such as carrier aggregation and network slicing.
- 2019: The 3GPP releases Release 17, which includes new features for 5G such as massive MIMO and millimeter wave.
- 2020: The 3GPP releases Release 18, which includes new features for 5G such as network slicing and edge computing.
- 2021: The 3GPP releases Release 19, which includes new features for 5G such as network slicing and edge computing.
- 2022: The 3GPP releases Release 20, which includes new features for 5G such as network slicing and edge computing.
5G is still a relatively new technology, and it is expected to continue to evolve over the coming years. As more 5G networks are deployed and more devices are connected to 5G networks, we can expect to see even more exciting new applications and use cases for 5G.
VII. 5G Security
5G security is a critical issue that needs to be addressed in order to ensure the safety and privacy of users. 5G networks are more vulnerable to cyberattacks than previous generations of networks due to their increased speed, capacity, and complexity.
There are a number of security risks associated with 5G networks, including:
- Denial-of-service attacks
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
- Spoofing attacks
- Eavesdropping attacks
- Malware attacks
In order to protect 5G networks from these attacks, a number of security measures need to be implemented, including:
- Strong authentication and authorization
- Encryption
- Network segmentation
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems
- Security awareness training
5G security is a complex issue, and there is no single solution that will protect 5G networks from all threats. However, by implementing a comprehensive security strategy, it is possible to mitigate the risks and protect 5G networks from cyberattacks.
5G Security
5G security is a critical issue that needs to be addressed in order to ensure the safety and reliability of 5G networks. 5G networks are more vulnerable to security threats than previous generations of networks due to their increased speed, complexity, and reliance on the cloud.
There are a number of security risks associated with 5G networks, including:
- Increased attack surface: 5G networks are more complex than previous generations of networks, which means that they have a larger attack surface. This makes them more vulnerable to attacks that exploit vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure.
- Increased data volume: 5G networks will carry a much larger volume of data than previous generations of networks. This makes them more attractive targets for attackers who are looking to steal data or disrupt services.
- Increased reliance on the cloud: 5G networks are more reliant on the cloud than previous generations of networks. This means that if the cloud is compromised, it could have a devastating impact on the entire network.
In order to address these security risks, 5G networks need to be designed with security in mind. This means that security must be built into the network from the ground up, and that security measures must be continuously updated and improved.
Some of the specific security measures that can be taken to protect 5G networks include:
- Using strong authentication and encryption
- Implementing security policies and procedures
- Monitoring the network for suspicious activity
- Using intrusion detection and prevention systems
- Backing up data regularly
By taking these steps, 5G networks can be made more secure and resistant to attack.
The cost of 5G is a major concern for many businesses and consumers. However, the cost of 5G is expected to come down over time as the technology matures and more devices are compatible with it.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the cost of 5G, including the cost of the infrastructure, the cost of the devices, and the cost of the service.
The cost of the infrastructure is one of the biggest factors in the cost of 5G. 5G networks require a denser network of antennas than 4G networks, which means that they are more expensive to build.
The cost of the devices is also a factor in the cost of 5G. 5G devices are more expensive than 4G devices, but this is expected to change over time as more devices are compatible with 5G.
The cost of the service is another factor in the cost of 5G. 5G service is more expensive than 4G service, but this is also expected to change over time as the technology matures and more providers offer 5G service.
Overall, the cost of 5G is a major concern, but it is expected to come down over time as the technology matures.
X. FAQ
Q: What is 5G?
A: 5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, and it promises to deliver much faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than previous generations of wireless technology.
Q: What are the benefits of 5G?
A: 5G has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and retail.
Q: What are the challenges of 5G?
A: There are a number of challenges associated with 5G, including the need for new infrastructure, the potential for interference with other wireless technologies, and the security risks associated with 5G networks.